Fire Load Calculation
Fire Load Calculation
Fire load’ is important for the fire risk assessment of any building. Which indicates the amount of heat released from everything inside the building to burn out completely. All buildings can be graded according to fire risk and appropriate fire warnings must be provided based on the fire load. Thus, buildings can be graded according to both fire load and fire resistance.
The formula for calculating fire load is as stated.
Fire load = Weight of Combustibles material in kg x calorific value of the material in Kcal/kg Floor area in square meters
For example, A fire load of one ton of ethane @ a calorific value of 52,220 KJ/Kg is stored in a place having a 100 square meter area.
Fire load = (1000 x 52220)/100
= 5,22,200 KJ/ m2
= 124808.79 kcal/m2
[ 1 Cal = 4.184 J ]
Here,
Weight of Combustibles material (Ethane) = 1 ton = 1000kg
Calorific value (Ethane) = 52,220 KJ/Kg
Area = 100 m2
The calculation of the fire load is the basis for determining the classification of the occupancies for the fire grading of buildings.
Fire grading of the structures:
The structural element of buildings is graded according to the time factor which is nearly equal to but does not exceed the test period in which the element fulfils its specified requirements. Accordingly, all structural elements have been graded under the following five categories depending upon their five resistance.
Grade 1…………………… 6 hours
Grade 2…………………… 4 hours
Grade 3…………………… 2 hours
Grade 4…………………… 1 hours
Grade 5…………………. 0.5 hours
Classification of Occupancies: The fire offices committee (U.K.), in its report of fire grading of buildings in 1946, has recognized 3 main classes of occupancies based on the fire load. This also conforms to the relevant Indian standard (I.S) specifications and may be stated as:
For classification of the various buildings according to the severity of the hazard:
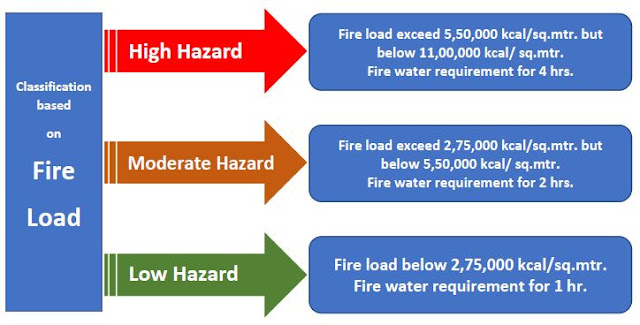
- Occupancies of low fire load:
Ordinary buildings for residential purposes, hotels, offices, schools, etc, or occupancies having a fire load not exceeding 2,75,000 kcal/sq.mtr of the net floor area of any compartment, nor exceeding an average of 550,000 kcal/sq.mtr on a limited isolated area. (for reference, the maximum for this type in F.P.S. system is 1,00,000 B.Th.U/sq.ft)
The fire resistance required by buildings of this category to withstand the complete burn-out of their contents without collapse is 1 hour as has been found after tests. Extensive investigations carried out in Switzerland and Germany have shown that the fire load in offices varies from 10 kg to 30 kg/sq.mtr wood equivalent to 43,356 to 130,068 kcal/sq.mtr whereas this type of occupancy has a one-hour rating with maximum fire loading up to 270,978 kcal/sq.mtr equivalent to 60 kg/sq.m.
- Occupancies of moderate fire load:
Retail shops, bazaars, stalls, factories, etc. hence the fire load exceeds, 2,75,000 kcal/sq.mtr, and is up to 550,000 kcal/sq.mtr. This is equivalent to the fire load of 2,75,000 kcal/sq.mtr, not exceeding an average of 11,00,000 kcal/sq.mtr on the limited isolated area as per relevant I.S. specifications. Occupancies of this type should have a fire resistance of two hours.
- Occupancies of high fire load:
Godowns, warehouses, etc. this category as per I.S. specifications exceed the fire load by 550,000 kcal/sq.mtr, but does not exceed an average of 11,00,000 kcal/sq.mtr of floor area. A fire resistance of 4 hours for these types of occupancies is considered sufficient. (for reference, the maximum for this type in F.P.S. system is 4,00,000 B.Th.U/sq.ft exceeding an average of 2,00,000 B.Th.U/sq.ft).
Example:
The manufacturing process industry uses the following material. Calculate the Fire load by using the following data:
Note: 1 calorie = 4.18 Joule
Fire load = Combustibles in kg x calorific value in kcal/kg ÷ Floor area in square meters
Fire load (paper) = (1000 x 3732.05)/10 = 373205.74 kcal/sq.mt
Fire load (wood) = (20000 x 4186.602)/20 = 418602 kcal/sq.mt
Fire load (coal) = (100,000 x 4784.688)/50 = 9569377.99 kcal/sq.mt
Fire load (rubber) = (5000 x 9569.37)/25 = 1913874 kcal/sq.mt
Fire load (Petroleum products) = (50,000 x 10287.081)/ 30 = 17145135.57 kcal/sq.mt
Total fire load = 2,94,20,195.3 kcal/sq.mt
The result indicates that the occupancy has a High fire load. So, fire resistance should be of 4hours.
To Calculate the Firewater Requirement:
Fire water supply, pumping capacity & other features of the firewater systems depend not only on the size of the risk but also on its fire growth & spread potentials, the risks are categorized under the following three classes.
- Low-hazard occupancies required at least one hour of firewater supply.
- Moderate hazard occupancies required at least a two-hour firewater supply.
- High-hazard occupancies required at least four hours of firewater supply
Installation of fire extinguishers:
Example:
1. Determine the number of fire extinguishers required to give adequate protection for a given property.
Risk: Light engineering workshop (Light hazard)
Area: 315m x 112 m. i.e. 35,280 sq. mtr.
Type of hazard: Class ‘A’ fire due to normal combustibles. As per IS 2190 this is Light Hazard so one 9 ltr water expelling extinguisher for every 600 sq.mtr of floor area should be installed. The extinguisher should be available within a 25 meter (82ft) radius.
Here Total area is 35,280 sq.mt.
So, no. of extinguisher = 35,280 sq.mt. /600 = 58.8 so, no. of extinguisher required is 59.
2. Determine the number of fire extinguishers required to give adequate protection for a given property.
Risk: Petroleum processing units (High hazard)
Area: 300m x 150 m. i.e. 45,000 sq. mtr.
Type of hazard: Class ‘B’ fire due to petroleum products. As per IS 2190, this is High Hazard so two 9 ltr foam chemical/mechanical types; or 5 kg capacity dry powder extinguishers for every 600 sq.mtr with a minimum of four extinguishers per compartment shall be installed. The extinguisher should be available within 15 mtr (49ft) radius.
Here Total area is 45000 sq.mt.
So, no. of extinguisher = 45000 sq.mt. /600 = 75 so, no. of extinguishers required is 75.
Reference of standards for Fire Load Calculation
There are in fact several reference standards (both prescriptive and performance-based codes or standards) available globally for the calculation of fire load. A few of them which are being used by the industry are listed below:
- NFPA 557, Standard for Determination of Fire Loads for Use in Structural Fire Protection Design
- National Building Code of India 2016 (NBC 2016) Part 4 Fire and Life Safety
- NFPA 551, Guide for the Evaluation of Fire Risk Assessments





Comments
Post a Comment